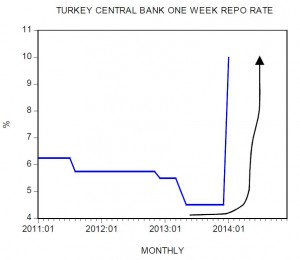
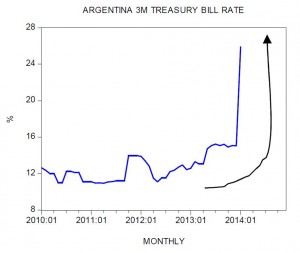
In countries such as Turkey and Argentina a tighter stance implemented by central banks has set in motion an economic bust. In Turkey the central bank has raised the one week repo rate to 10 percent from 4.5 percent while in Argentina the 3-month Treasury bill rate climbed to 25.89 percent from 16 percent in early January. In Argentina an increase in rates took place once the central bank aggressively curbed its monetary pumping, while in Turkey the central bank raised its policy rate.
What prompted the tighter stance? The main reason was the sharp decline in the exchange rate of domestic currencies against the US dollar. The Turkish lira fell to 2.39 per US dollar from 1.76 liras in January last year — a depreciation of almost 36 percent. The price of the US dollar in terms of the Argentina peso jumped to 8 pesos from 5 pesos in January last year — an increase of 60 percent. Note that in the black market the price of the US dollar stood at 12.5 pesos.
The catalyst for the currency depreciation in both economies has been strong increases in the money supply on account of the loose monetary policies of the respective central banks. In Turkey the yearly rate of growth of AMS stood at 30 percent in August this year while in Argentina the yearly rate of growth stood at 40 percent. The underlying currency rate of exchange is set in motion by the relative increases in the money supply. This means that if Turkey and Argentina allow their money supply rate of growth to exceed the rate of growth of the US money supply, both Turkey’s and Argentina’s currency will weaken against the US dollar.
Observe that in Turkey and Argentina the strong increase in the money supply rate of growth was accompanied by strong increases in so called real GDP. In Turkey by Q1 2010 the yearly rate of growth stood at 12.6 percent while in Argentina in Q2 2010 the rate of growth stood at 11.8 percent. Given that GDP reflects changes in the money supply rate of growth we suggest that the growth in GDP mirrors the build-up of bubble activities. The stronger the GDP the stronger the pace of bubble formation is. Obviously then a tighter monetary stance is going to undermine the rate of growth of money supply and thus weaken the support for various bubble activities. It is this that sets in motion an economic bust. We suggest that a similar scenario is awaiting other economies that have been generating a strong real GDP rate of growth by means of monetary pumping.
This article was previously published at Mises.org.








Isn’t Argentina a laboratory for Modern Monetary Theory? If a sovereign country that prints its own money can never be broke, every Argentine should be shopping for a yacht right now. What gives?
chuck martel – quite correct.
The situation in Argentina is quite different to what you are suggesting because Argentina’s debt is USD denominated rather than in its own currency. MMT talks about debts in the country’s own currency, which are easliy repayable by printing more currency. I am not saying that non stop printing is a good idea by the way and am not an MMT’er.